Table of Contents
cs20pf22as13: Path Finding
Goals
- Apply your knowledge of graphs and related algorithms to a real-world problem.
- Define a class with methods that can produce driving directions.
Prerequisites
This assignment requires familiarity with the lecture materials presented in class through week 13.
Background
Quoth the arbiter of all human information:
The international E-road network is a numbering system for roads in Europe developed by the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE). The network is numbered from E1 up and its roads cross national borders. It also reaches Central Asian countries like Kyrgyzstan, since they are members of the UNECE.
GitHub user Lasse Westh-Nielsen posted a CSV representation of much of the E-road network in September of 2016. A slightly modified version of this data (with country names more amenable to Google Maps) is available on our server in file /srv/datasets/e-roads.csv.
Each of the 1239 lines in the file consists of 7 comma-delimited tokens describing a road segment:
- A road number, e.g.
E05 - An origin country name, e.g.
Denmark - An origin place name, e.g.
Ålborg - A destination country name
- A destination place name
- The distance of the segment (as an integer in km)
- Whether the segment is a water crossing (
trueorfalse)
Here are the lines from the file regarding E-road E5:
E05,UK,Greenock,UK,Glasgow,40,false E05,UK,Glasgow,UK,Gretna,142,false E05,UK,Gretna,UK,Carlisle,16,false E05,UK,Carlisle,UK,Penrith,40,false E05,UK,Penrith,UK,Preston,109,false E05,UK,Preston,UK,Warrington,49,false E05,UK,Warrington,UK,Birmingham,128,false E05,UK,Birmingham,UK,Newbury,166,false E05,UK,Newbury,UK,Southampton,71,false E05,UK,Southampton,France,Le Havre,207,true E05,France,Le Havre,France,Paris,196,false E05,France,Paris,France,Orléans,134,false E05,France,Orléans,France,Tours,118,false E05,France,Tours,France,Poitiers,101,false E05,France,Poitiers,France,Bordeaux,256,false E05,France,Bordeaux,Spain,San Sebastián,243,false E05,Spain,San Sebastián,Spain,Burgos,246,false E05,Spain,Burgos,Spain,Madrid,250,false E05,Spain,Madrid,Spain,Cordóba,391,false E05,Spain,Cordóba,Spain,Sevilla,141,false E05,Spain,Sevilla,Spain,Cádiz,122,false E05,Spain,Cádiz,Spain,Algeciras,117,false
For the purposes of this assignment, consider each road segment to be an undirected (or bidirectional) edge in a graph representing the E-road network.
Assignment
You shall define a class named ERoadNetwork in a module named e_roads, instances of which contain a method to determine the shortest path between two locations in the road network defined by file e-roads.csv, optionally excluding water crossings.
Method shortest_path() accepts two string arguments of the form 'place_name, country_name' and returns the shortest path between those places in three different forms, e.g. for the shortest path between Greenock, UK and Edinburgh, UK:
- A tuple of place names along the path:
('Greenock, UK', 'Glasgow, UK', 'Edinburgh, UK')
- A tuple of segments for each road traveled:
(('E05', ('Greenock, UK', 'Glasgow, UK')), ('E16', ('Glasgow, UK', 'Edinburgh, UK')))
- A string formatted to be a Google Maps URL requesting directions between the place names:
'https://www.google.com/maps/dir/Greenock,+UK/Glasgow,+UK/Edinburgh,+UK'
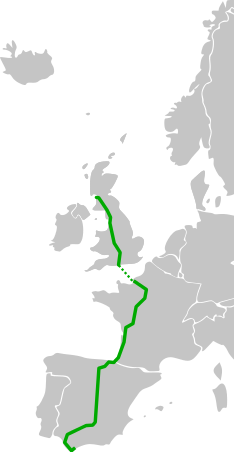
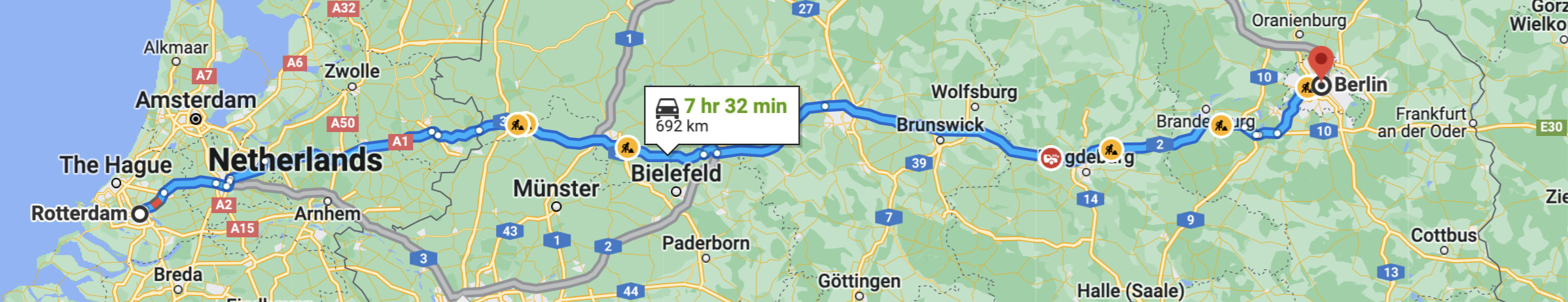
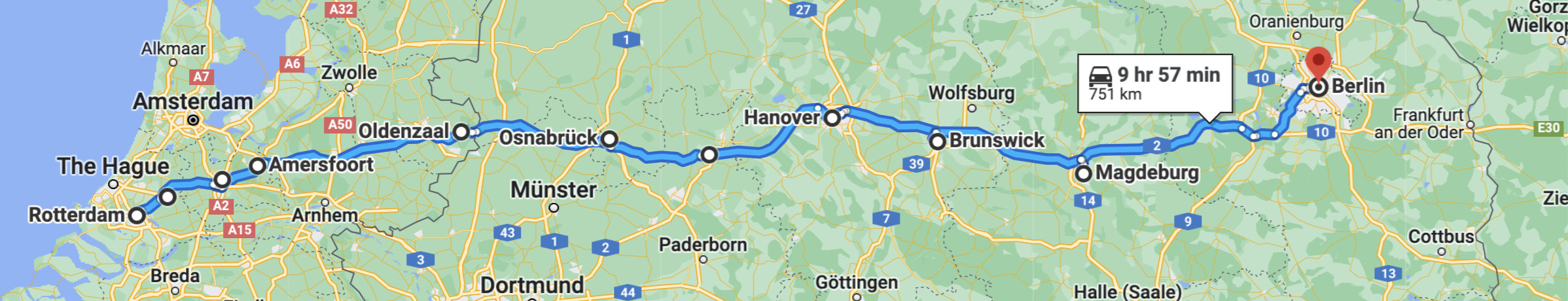
The paths should look relatively sane compared with Google Maps' suggested driving directions, though there will likely be many differences due to the small dataset we are using:
Specifications
Use the following skeleton code as a template for your class. Several doctests are included for testing purposes, and to demonstrate the expected return value of method shortest_path(). Note the potentially different paths when water crossings are included vs. excluded.
- e_roads.py
""" CS 20P: Shortest paths in the international E-road network. """ import collections import heapq import sys class ERoadNetwork: """ Graph-based representation of the E-road network. """ def __init__(self, include_water=True): """ Initializes a path-finding object, optionally excluding water crossings. """ pass # TODO def shortest_path(self, src: str, dst: str) -> tuple[tuple, tuple, str] | None: """ Returns several representations of the shortest path from `src` to `dst`. :param src: the starting location :param dst: the ending location :return: `None` if no path exists, or a tuple of three representations of the shortest path, as in the doctests below: >>> path_finder = ERoadNetwork() >>> import pprint >>> pprint.pprint(path_finder.shortest_path('Greenock, UK', 'Edinburgh, UK')) (('Greenock, UK', 'Glasgow, UK', 'Edinburgh, UK'), (('E05', ('Greenock, UK', 'Glasgow, UK')), ('E16', ('Glasgow, UK', 'Edinburgh, UK'))), 'https://www.google.com/maps/dir/Greenock,+UK/Glasgow,+UK/Edinburgh,+UK') >>> pprint.pprint(path_finder.shortest_path('Stockholm, Sweden', 'Tallinn, Estonia')) (('Stockholm, Sweden', 'Tallinn, Estonia'), (('E20', ('Stockholm, Sweden', 'Tallinn, Estonia')),), 'https://www.google.com/maps/dir/Stockholm,+Sweden/Tallinn,+Estonia') >>> land_only = ERoadNetwork(include_water=False) >>> pprint.pprint(land_only.shortest_path('Stockholm, Sweden', 'Tallinn, Estonia')) (('Stockholm, Sweden', 'Sundsvall, Sweden', 'Umeå, Sweden', 'Luleå, Sweden', 'Haparanda, Sweden', 'Tornio, Finland', 'Kemi, Finland', 'Oulu, Finland', 'Jyväskylä, Finland', 'Lahti, Finland', 'Helsinki, Finland', 'Vaalimaa, Finland', 'Sankt-Peterburg, Russia', 'Tallinn, Estonia'), (('E04', ('Stockholm, Sweden', 'Sundsvall, Sweden', 'Umeå, Sweden', 'Luleå, Sweden', 'Haparanda, Sweden', 'Tornio, Finland', 'Kemi, Finland')), ('E75', ('Kemi, Finland', 'Oulu, Finland', 'Jyväskylä, Finland', 'Lahti, Finland', 'Helsinki, Finland')), ('E18', ('Helsinki, Finland', 'Vaalimaa, Finland', 'Sankt-Peterburg, Russia')), ('E20', ('Sankt-Peterburg, Russia', 'Tallinn, Estonia'))), 'https://www.google.com/maps/dir/Stockholm,+Sweden/Sundsvall,+Sweden/Umeå,+Sweden/Luleå,+Sweden/Haparanda,+Sweden/Tornio,+Finland/Kemi,+Finland/Oulu,+Finland/Jyväskylä,+Finland/Lahti,+Finland/Helsinki,+Finland/Vaalimaa,+Finland/Sankt-Peterburg,+Russia/Tallinn,+Estonia') """ pass # TODO
Sample Executable
Sample executable cs20p_e_roads exists on the server and prints the expected path and Google Maps URL given two locations as command-line arguments, optionally excluding water crossings if you add a third command-line argument:
% cs20p_e_roads 'Greenock, UK' 'Madrid, Spain' Greenock, UK Glasgow, UK Gretna, UK Carlisle, UK Penrith, UK Preston, UK Warrington, UK Birmingham, UK Newbury, UK Southampton, UK Le Havre, France Paris, France Orléans, France Tours, France Poitiers, France Bordeaux, France San Sebastián, Spain Burgos, Spain Madrid, Spain https://www.google.com/maps/dir/Greenock,+UK/Glasgow,+UK/Gretna,+UK/Carlisle,+UK/Penrith,+UK/Preston,+UK/Warrington,+UK/Birmingham,+UK/Newbury,+UK/Southampton,+UK/Le+Havre,+France/Paris,+France/Orléans,+France/Tours,+France/Poitiers,+France/Bordeaux,+France/San+Sebastián,+Spain/Burgos,+Spain/Madrid,+Spain % cs20p_e_roads 'Greenock, UK' 'Madrid, Spain' uh oh No path from Greenock, UK to Madrid, Spain!
Map Demo
(Geocoding for this map was done using the Google Geocoding API, which may not exactly match the intent of some of these place names. But should be roughly correct.)
cs20p_e_roads "Greenock, UK" "Madrid, Spain"
Submission
Submit e_roads.py via turnin.
 Feedback Robot
Feedback Robot
This project has a feedback robot that will run some tests on your submission and provide you with a feedback report via email within roughly one minute.
Please read the feedback carefully.
Due Date and Point Value
Due at 23:59:59 on the date listed on the syllabus.
Assignment 13 is worth 60 points.
Possible point values per category: --------------------------------------- Correct paths, with/without water: Between place names 20 Broken into roads 20 As a Google Maps URL 20 Possible deductions: Style and practices 10–20% Possible extra credit: Submission via Git 5% ---------------------------------------